- What is Business as Usual (BAU)? - October 8, 2025
- How Slack Grew to 10M Users Without Ads: Complete Growth Blueprint - October 8, 2025
- Top Startups in Kerala 2025 - September 26, 2025
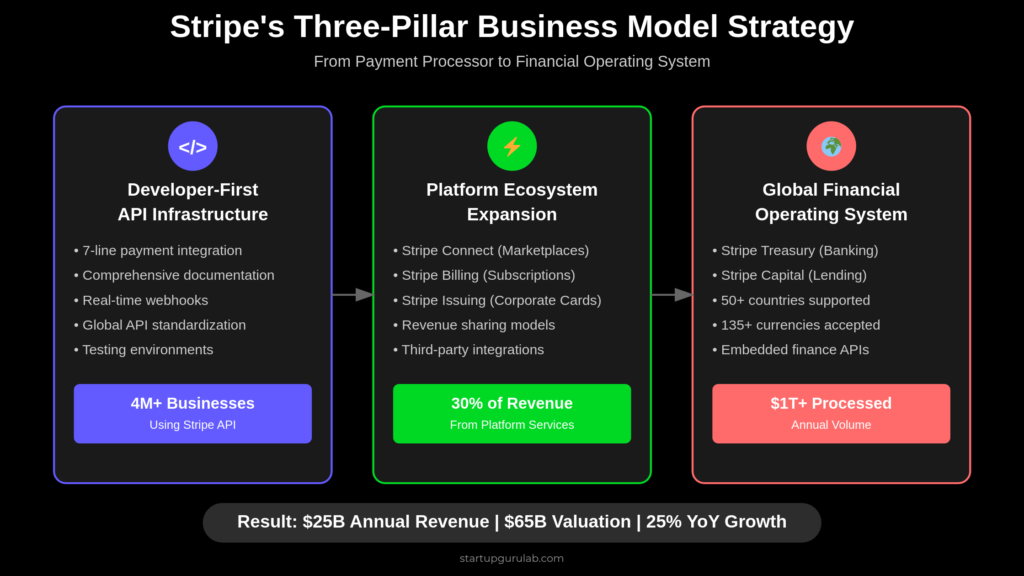
In 2024, Stripe achieved an estimated $25 billion in annual revenue, processing over $1 trillion in payment volume—representing a 25% year-over-year growth rate despite economic headwinds. What makes this achievement remarkable is that Stripe accomplished this milestone by fundamentally reimagining payment infrastructure as a platform business model, transforming from a simple payment processor into a comprehensive financial operating system for internet businesses.
Founded in 2010 by Irish brothers Patrick and John Collison, Stripe has grown from a Y Combinator startup to a $65 billion valuation by building developer-first payment infrastructure that enabled the creation of entire digital economy categories—from subscription businesses to marketplace platforms to embedded finance applications.
Rather than competing solely on processing fees, Stripe pioneered a platform approach that monetizes every aspect of online business operations through an expanding ecosystem of financial products and services. This strategy enabled the company to achieve industry-leading take rates while becoming mission-critical infrastructure for over 4 million businesses worldwide, from startups to Fortune 500 companies.
This case study analyzes Stripe’s revolutionary business model that enabled two college dropouts to build one of the world’s most valuable private companies while creating the foundational infrastructure that powers the modern internet economy.

Executive Summary
- Company: Stripe, Inc. (Founded 2010)
- Challenge: Modernizing complex, outdated payment infrastructure for internet businesses
- Strategy: Developer-first platform with expanding financial services ecosystem
- Timeline: 2010-2024 (14 years to $25B revenue)
Results:
- $25B estimated annual revenue in 2024 (25% growth from 2023)
- $65B valuation making it one of the most valuable private companies
- 4+ million businesses using Stripe globally
- $1+ trillion in annual payment volume processed
- 50+ countries and territories supported
- 135+ currencies accepted
Main Takeaway: Platform business models that solve fundamental infrastructure problems can achieve massive scale by expanding from core products into comprehensive ecosystems, especially when targeting developers and enabling new business model categories rather than just optimizing existing processes.
Stripe Background & The Payment Processing Landscape
Pre-Stripe Market Reality
Before Stripe’s developer-first approach gained traction, the payment processing market was dominated by legacy providers with antiquated approaches:
Traditional Payment Processing Problems:
- Complex integration requiring weeks or months of development time
- Enterprise-focused sales processes with lengthy contract negotiations
- Limited international support requiring separate provider relationships
- Inflexible pricing models with hidden fees and minimum volume requirements
- Poor developer experience with outdated APIs and documentation
Small Business Pain Points:
- High barriers to accepting online payments for new businesses
- Customer acquisition costs increased by complex checkout processes and payment failures
- Limited access to payment analytics and financial insights
- No integrated solutions for subscription billing, marketplace payments, or international expansion
- Vendor lock-in through proprietary systems and data portability limitations
Emerging Opportunities in the Digital Economy
When Stripe launched in 2010, several market shifts created opportunities for a new approach:
Technology Enablers:
- API-first architecture becoming standard for software development
- Mobile and e-commerce adoption accelerating globally
- Cloud infrastructure enabling rapid scaling and international expansion
- Developer-as-buyer trend with technical decision makers controlling vendor selection
Market Dynamics:
- Subscription economy emergence requiring sophisticated billing and revenue management
- Marketplace platforms creating new payment flow complexities
- Growing acceptance of API-first solutions across enterprise software categories
- International expansion becoming critical for digital business growth
Stripe’s Foundational Insight
Patrick and John Collison identified a critical market opportunity that established players couldn’t address effectively:
Key Hypothesis: “If we can make payment integration as simple as adding seven lines of code, we can enable entirely new categories of internet businesses while capturing increasing share of online commerce through superior developer experience.”
This insight drove three foundational decisions:
- Build API-first infrastructure rather than traditional payment terminals
- Target developers rather than business decision makers
- Expand beyond payments into comprehensive financial infrastructure
Strategic Approach: Developer-First Platform Business Model
Stripe chose a revolutionary platform-first growth strategy that prioritized developer experience and API simplicity to create network effects and platform lock-in that traditional payment processors couldn’t replicate.
Category Creation Strategy Rationale
Why Developer-First Positioning Worked:
- Reduced sales cycles by targeting technical implementers rather than procurement teams
- Created viral adoption through developer word-of-mouth and community evangelism
- Enabled rapid international expansion through standardized API rather than local partnerships
- Built defensible moats through integration complexity and switching costs
- Generated platform effects where ecosystem growth increased Stripe’s value proposition
Learn more about building viral growth mechanisms that create systematic adoption loops for new categories.
Stripe’s Revenue Model: The Complete Breakdown
Primary Revenue Stream: Payment Processing (70% of Revenue)
Core Processing Fees:
- Standard rate: 2.9% + 30¢ per successful transaction
- International cards: Additional 1% fee
- American Express: Additional 0.8% surcharge
- Disputed payments: $15 per chargeback
Volume-Based Pricing:
- Interchange Plus pricing for high-volume merchants
- Custom rates for enterprises processing $1M+ monthly
- Blended rates ranging from 2.4% to 2.9% based on volume and geography
2024 Revenue Impact:
- Estimated $17.5B from core payment processing
- Average take rate of 1.75% across all payment volume
- Processing fees represent 70% of total company revenue
Secondary Revenue Streams: Platform Services (30% of Revenue)
Stripe Billing (Subscription Management):
- 0.5% additional fee on subscription payments
- Usage-based billing and metered pricing support
- Revenue recognition and accounting automation
- Estimated $2.5B annual revenue from subscription commerce
Stripe Connect (Marketplace Payments):
- Platform fee sharing model taking 0.25% of marketplace volume
- Additional fees for Express and Custom account types
- International transfer fees for cross-border marketplace payments
- Estimated $1.8B annual revenue from marketplace platforms
Stripe Issuing (Corporate Cards):
- $15-50 per card issuance fee
- Interchange revenue sharing from card usage
- Monthly maintenance fees for enterprise programs
- Estimated $800M annual revenue from card issuing
Additional Revenue Sources:
- Stripe Capital (business lending): Revenue sharing from loan payments
- Stripe Treasury (embedded banking): Fees on API-driven banking services
- Stripe Identity (verification): Per-verification fees
- Professional services and consulting: Custom integration support
Business Model Canvas Analysis
Value Propositions
For Developers:
- Seven-line integration for payment acceptance
- Comprehensive API documentation and developer tools
- Standardized international payment support
- Real-time webhooks and robust testing environments
For Businesses:
- Rapid time-to-market for payment-enabled applications
- Unified platform for global commerce operations
- Advanced fraud protection and security compliance
- Detailed analytics and revenue optimization tools
For Platforms and Marketplaces:
- Split payment functionality for multi-party transactions
- Automated onboarding for platform participants
- Compliance management for regulated industries
- Revenue sharing and fee distribution automation
Customer Segments
Primary Segments:
- Software developers and technical teams: Direct integration decision makers
- Digital-first businesses: E-commerce, SaaS, subscription, and marketplace companies
- Enterprise platforms: Large companies building embedded financial products
- International businesses: Companies requiring global payment infrastructure
Segment Growth Rates:
- SMB e-commerce: 35% annual growth
- SaaS and subscription: 40% annual growth
- Marketplace platforms: 50+ annual growth
- Enterprise embedded finance: 60%+ annual growth
Key Partnerships
Technology Integrations:
- E-commerce platforms: Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento
- Business software: Salesforce, HubSpot, QuickBooks
- Development frameworks: React, Node.js, Python libraries
Financial Infrastructure:
- Banking partners for Treasury and Issuing products
- Card networks: Visa, Mastercard, American Express
- Regional payment methods: Alipay, WeChat Pay, SEPA
Strategic Alliances:
- Cloud providers: AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure
- Professional services: Accenture, Deloitte for enterprise implementations
Compare this partnership approach with typical startup growth frameworks to understand Stripe’s ecosystem advantages.
Stripe Growth Strategy & Monetization Evolution
Phase 1: Developer-First Foundation (2010-2015)
Product Development:
- API-first payment processing with focus on integration simplicity
- Comprehensive developer documentation and testing tools
- Real-time webhooks and robust error handling
- International expansion supporting multiple currencies and payment methods
Go-to-Market Strategy:
- Developer evangelism through conferences, hackathons, and technical content
- Word-of-mouth growth through superior developer experience
- Partnership integrations with popular e-commerce and development platforms
- Transparent pricing without hidden fees or minimum volume requirements
Key Metrics (End of 2015):
- $20B annual payment volume processed
- Thousands of businesses using Stripe globally
- Processing fees averaging 2.9% + 30¢ per transaction
- Expansion to 25+ countries with local payment method support
Phase 2: Platform Expansion and Enterprise Growth (2016-2020)
Product Sophistication:
- Stripe Billing launch enabling subscription and usage-based billing
- Stripe Connect introduction for marketplace and platform payments
- Advanced fraud protection with machine learning-powered risk scoring
- Stripe Issuing beta for corporate card programs
Market Expansion:
- Enterprise sales team development for large-scale implementations
- International expansion accelerating with local partnerships
- Vertical-specific solutions for industries like transportation and hospitality
- Platform partnerships enabling embedded payment experiences
Business Model Evolution:
- Revenue diversification beyond core payment processing
- Higher take rates through value-added services
- Platform fees from Connect and Billing products
- Custom pricing for enterprise customers
Growth Metrics (End of 2020):
- $640B annual payment volume processed
- $7.4B estimated annual revenue
- 2+ million businesses using Stripe globally
- $36B valuation in funding rounds
Phase 3: Financial Operating System (2021-2024)
Product Innovation:
- Stripe Treasury enabling embedded banking for platforms
- Stripe Capital providing business lending to platform participants
- Stripe Climate for carbon removal marketplace
- Advanced international features including local acquiring
Strategic Positioning:
- Evolution from payment processor to comprehensive financial infrastructure
- Platform business model enabling ecosystem participants to build financial products
- Global expansion with local entity establishment in key markets
- Enterprise feature development for large-scale implementations
Current Performance (2024):
- $1+ trillion annual payment volume processed
- $25B estimated annual revenue
- $65B valuation making it one of the most valuable private companies
- 4+ million businesses across 50+ countries
Learn how to track these types of metrics using proven startup KPI frameworks for platform businesses.
Stripe Revenue Growth Trajectory & Financial Metrics
Revenue Evolution
Historical Growth:
- 2015: $450M estimated revenue
- 2018: $2.5B estimated revenue
- 2020: $7.4B estimated revenue
- 2022: $12.9B estimated revenue
- 2024: $25B estimated revenue (25% growth)
Revenue Composition (2024):
- Payment processing: $17.5B (70%)
- Stripe Billing: $2.5B (10%)
- Stripe Connect: $1.8B (7%)
- Other services: $3.2B (13%)
Key Financial Metrics
Unit Economics:
- Average take rate: 1.75% across all processed volume
- Customer lifetime value: $180K+ for enterprise accounts
- Net revenue retention: 119% annually
- Gross margin: 45-50% across all products
Scale Indicators:
- Processing volume growth: 25% annually
- Average transaction size: $47 globally
- International volume: 40% of total processing
- Platform transactions: 35% of total volume
Valuation Metrics:
- Revenue multiple: 2.6x ($65B valuation on $25B revenue)
- Growth-adjusted PEG ratio competitive with public fintech companies
- Private market comparisons suggesting continued premium valuation
Compare these results with industry acquisition cost benchmarks to understand Stripe’s platform efficiency.
Key Strategic Insights & Lessons
1. API-First Platform Strategy
Strategic Decision: Building developer-centric APIs rather than business user interfaces as primary product experience.
Why It Worked:
- Reduced integration complexity from months to hours
- Created viral adoption through developer word-of-mouth
- Enabled rapid international scaling through standardized infrastructure
- Built switching costs through integration depth and complexity
- Generated network effects where ecosystem growth improved platform value
Lesson for Startups: Platform strategies targeting technical buyers can create stronger adoption and defensibility than traditional business-focused approaches, especially for infrastructure products.
2. Expanding Platform Ecosystem vs. Core Product Focus
Strategic Decision: Systematically expanding from payments into adjacent financial services rather than optimizing core processing.
Revenue Impact:
- Platform services generating 30% of total revenue by 2024
- Higher margins on value-added services compared to commodity processing
- Customer lock-in through multi-product usage and integration complexity
- Upselling opportunities across expanded product portfolio
Lesson for Startups: Platform expansion into adjacent categories can dramatically increase customer lifetime value and competitive differentiation when core products have strong adoption and switching costs.
3. International-First Architecture
Strategic Decision: Building global infrastructure from the beginning rather than expanding domestically first.
Competitive Advantages:
- First-mover advantage in emerging markets with growing e-commerce adoption
- Standardized API reducing integration complexity for international businesses
- Currency and payment method diversity creating barrier to competitive switching
- Local compliance and regulatory expertise building trust with enterprise customers
Lesson for Startups: International-first approaches can create significant competitive moats and market expansion opportunities, especially for digital infrastructure businesses where local presence requirements are minimal.
Implementation Framework for Platform Business Models
When Stripe’s Platform Strategy Applies
Use this approach when:
- Product solves fundamental infrastructure problems with high switching costs
- Target customers are technical decision makers with API integration capabilities
- Market opportunity exists for adjacent products and services
- Developer experience can create viral adoption and word-of-mouth growth
- Network effects exist where platform growth increases value for all participants
Avoid this approach when:
- Product requires extensive human interaction and custom implementation
- Target market lacks technical sophistication for API integration
- Competitive advantages depend on local relationships and manual processes
- Regulatory requirements prevent standardized platform approaches
Replicable Framework Elements
1. Developer Experience Strategy
API Design Principles:
- Prioritize integration simplicity over feature comprehensiveness
- Provide extensive documentation, testing tools, and code examples
- Implement real-time webhooks and robust error handling
- Build SDKs and libraries for popular programming languages
Community Development:
- Create developer evangelism programs and technical content marketing
- Sponsor hackathons, conferences, and open source projects
- Build partnership integrations with popular development frameworks
- Implement feedback loops for API improvement and feature prioritization
2. Platform Expansion Planning
Adjacent Product Strategy:
- Identify natural expansion opportunities within customer workflows
- Build platform infrastructure enabling third-party development
- Create revenue sharing models for ecosystem participants
- Develop marketplace features connecting platform users
Enterprise Feature Development:
- Implement white-label and custom branding capabilities
- Build advanced analytics and reporting for platform managers
- Create compliance and regulatory features for enterprise requirements
- Develop custom pricing and billing models for large-scale usage
Implement data-driven growth frameworks to optimize platform expansion strategies.
3. International Scaling Framework
Global Infrastructure Development:
- Build multi-region API infrastructure for performance and compliance
- Implement local payment methods and currency support
- Develop relationships with regional banking and financial partners
- Create localized documentation and customer support
Regulatory Compliance Strategy:
- Establish legal entities in key markets for local compliance
- Build automated compliance monitoring and reporting systems
- Develop partnerships with local regulatory and legal experts
- Implement data localization and privacy protection features
Action Plan: Building a Platform Business Model
Phase 1: Core Platform Foundation (Months 1-12)
Technical Infrastructure:
- Build robust API architecture optimized for developer experience
- Implement comprehensive testing, documentation, and monitoring systems
- Develop SDK libraries for popular programming languages and frameworks
- Create sandbox and testing environments for developer adoption
Market Validation:
- Identify core use case solving fundamental infrastructure problem
- Build initial customer base through superior technical implementation
- Gather feedback for API improvement and feature prioritization
- Establish pricing model balancing adoption with sustainable unit economics
Use our customer acquisition strategy guide to plan developer-focused growth approaches.
Phase 2: Ecosystem Development and Platform Effects (Months 13-36)
Platform Expansion:
- Identify adjacent products and services within customer workflows
- Build partnership integrations with complementary platforms and tools
- Develop marketplace features enabling ecosystem participant connections
- Implement revenue sharing models for platform-enabled transactions
Developer Community Growth:
- Launch developer evangelism programs and technical content marketing
- Create educational resources, tutorials, and best practice documentation
- Build feedback mechanisms for API enhancement and feature development
- Establish community forums and support channels
Apply three-pillar domain authority strategies for technical thought leadership positioning.
Phase 3: Enterprise Expansion and Global Scale (Months 37+)
Enterprise Feature Development:
- Build white-label and custom implementation capabilities
- Develop advanced analytics, reporting, and business intelligence features
- Create compliance and regulatory features for enterprise requirements
- Implement custom pricing and billing models for large-scale customers
International Market Expansion:
- Establish local presence in key markets for compliance and partnerships
- Build region-specific features including payment methods and currencies
- Develop relationships with local banking, regulatory, and technology partners
- Create localized customer success and technical support capabilities
Success Metrics to Track
Platform Growth Metrics:
- API adoption rates and integration completion percentages
- Developer community growth and engagement levels
- Platform transaction volume and revenue per customer
- Ecosystem participant growth and activity levels
Track these against startup metric benchmarks for your industry and stage.
Business Performance Indicators:
- Take rate optimization and revenue per transaction
- Customer lifetime value and net revenue retention rates
- Market share growth in target segments and geographies
- Platform ecosystem revenue contribution and growth rates
Conclusion: The Platform Infrastructure Playbook
Stripe’s journey to $25 billion in revenue demonstrates that platform business models targeting infrastructure problems can achieve extraordinary scale and defensibility when they prioritize developer experience, systematic ecosystem expansion, and international architecture from inception. By building API-first payment infrastructure rather than traditional business tools, focusing on technical decision makers over procurement teams, and expanding into adjacent financial services, Stripe created sustainable competitive advantages that traditional providers couldn’t replicate.
The key insight for startups: Platform approaches targeting fundamental infrastructure problems can achieve massive scale through superior technical implementation and systematic ecosystem development. Stripe’s systematic approach proves that:
- Developer-first strategies create viral adoption and strong switching costs through superior technical implementation
- Platform expansion into adjacent categories dramatically increases customer lifetime value and competitive differentiation
- International-first architecture enables rapid global scaling and market leadership across diverse geographies
- API-centric business models reduce traditional sales friction while building deeper customer integration
- Infrastructure platforms benefit from network effects where ecosystem growth increases value for all participants
For startups targeting technical buyers and infrastructure markets, Stripe’s playbook provides a proven framework for building platform businesses that scale through technical excellence and ecosystem development rather than traditional sales and marketing approaches.
The platform infrastructure opportunity exists in every industry where developers are building the next generation of business applications and require reliable, scalable infrastructure services.
Ready to implement platform-first growth strategies?
Learn more about building viral growth loops that create sustainable competitive advantages through developer communities.
Compare your metrics with startup benchmarks by industry to set realistic growth targets for platform businesses.
Discover domain authority strategies for building technical thought leadership in competitive markets.
Understand customer acquisition optimization for developer-focused platforms and API-driven growth models.

