- What is Business as Usual (BAU)? - October 8, 2025
- How Slack Grew to 10M Users Without Ads: Complete Growth Blueprint - October 8, 2025
- Top Startups in Kerala 2025 - September 26, 2025
In February 2025, Zoho Corporation achieved a remarkable $12.5 billion valuation according to the Burgundy Private Hurun India 500 report—representing a 58% increase from the previous year. But what makes this achievement extraordinary isn’t just the numbers—it’s that Zoho reached this milestone through a completely bootstrapped approach that defies conventional Silicon Valley wisdom.
Founded in 1996 by Sridhar Vembu and Tony Thomas, Zoho has grown from a small apartment-based startup to $1.4 billion in annual revenue without raising external funding, going public, or following traditional venture capital playbooks. Instead, the Chennai-based SaaS company pioneered what founder Sridhar Vembu calls “transnational localism”—building world-class software products from rural India while maintaining complete independence and profitability.
This case study analyzes Zoho’s unconventional growth strategy that enabled the company to compete successfully against tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Salesforce while building a sustainable business model that prioritizes long-term value creation over rapid expansion and exit strategies.

Executive Summary
- Company: Zoho Corporation (Founded 1996)
- Challenge: Competing against tech giants with unlimited resources while remaining bootstrapped
- Strategy: Rural-first development combined with comprehensive suite strategy
- Timeline: 1996-2025 (29 years to $12.5B valuation)
Results:
- $1.4B annual revenue in 2024 (800% growth from 2016)
- $12.5B valuation (58% increase in 2024)
- 100+ million users across 700,000+ businesses in 150+ countries
- 25,000+ employees with 15% from rural training programs
- Zero external funding – completely bootstrapped and profitable
- 100+ integrated applications in comprehensive business suite
Main Takeaway:
Sustainable growth strategies that prioritize customer value, employee well-being, and long-term independence can achieve remarkable scale without sacrificing core values or operational freedom, even when competing against venture-backed giants with significantly more resources.
Background & The Enterprise Software Landscape
Pre-Zoho Market Reality
Before Zoho’s comprehensive suite approach gained traction, the business software market was dominated by fragmented, expensive solutions:
Traditional Enterprise Software Problems:
- High costs: Enterprise software licensing required significant upfront investments
- Complex integrations: Different vendors for CRM, email, accounting, and productivity tools
- Vendor lock-in: Proprietary systems with limited interoperability
- Urban-centric development: All major tech companies concentrated in expensive metropolitan areas
- Short-term focus: Quarterly earnings pressure driving product decisions over customer needs
SMB Market Gaps:
- Limited affordable options for comprehensive business management
- Customer acquisition costs averaging $205 for SaaS companies made serving smaller businesses uneconomical
- Complex implementation processes requiring specialized IT expertise
- Lack of integrated solutions forcing businesses to manage multiple vendor relationships
Emerging Opportunities in the SaaS Era
When Zoho began its transformation from AdventNet (network management tools) to a comprehensive business suite in the early 2000s, several market shifts created opportunities:
Technology Enablers:
- Cloud computing reducing infrastructure costs and complexity
- Web-based applications eliminating installation and maintenance overhead
- API-first development enabling easier integrations
- Mobile internet expanding global market reach
Market Dynamics:
- SMBs increasingly adopting cloud solutions for cost efficiency
- Growing demand for integrated business management platforms
- India’s software market expanding at 15-20% annually
- Rural talent pools remaining largely untapped by tech industry
Zoho’s Foundational Insight
Sridhar Vembu and his team identified a critical market opportunity that established players couldn’t address effectively:
Key Hypothesis: “If we can build comprehensive, affordable business software while maintaining complete independence from external investors, we can serve customers that big companies find unprofitable while building a sustainable, long-term business.”
This insight drove three foundational decisions:
- Remain bootstrapped to maintain operational freedom and customer-first focus
- Build comprehensive suites rather than competing on individual features
- Develop from rural areas to access untapped talent while reducing operational costs
Strategic Approach: Bootstrapped Suite-First Category Creation
Zoho chose a unique category creation strategy that combined comprehensive business suites with rural development, creating a sustainable competitive advantage that traditional venture-backed companies couldn’t replicate.
Category Creation Strategy Rationale
Why “Operating System for Business” Positioning Worked:
- Clear differentiation: Integrated suite vs. point solutions created distinct value proposition
- Cost advantage: Bootstrapped model enabled aggressive pricing without investor pressure
- Sustainable development: Rural offices provided cost efficiency and talent access
- Long-term focus: Freedom to invest in R&D and customer success over growth metrics
- Cultural alignment: Indian frugality and long-term thinking resonated globally
Learn more about when to choose different customer acquisition approaches based on market conditions and business models.
Five-Pillar Bootstrapped Growth Strategy
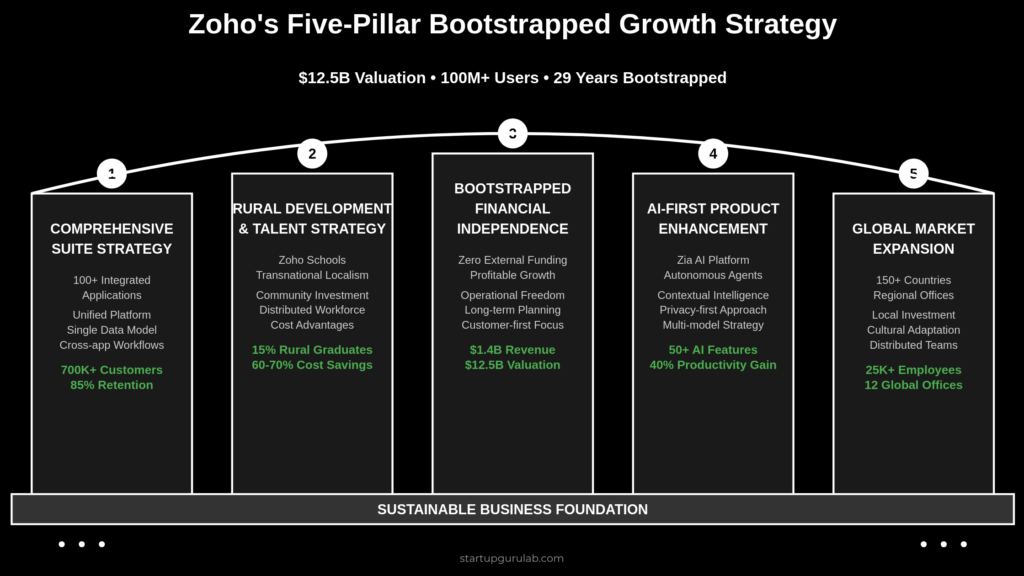
Pillar 1: Comprehensive Suite Strategy
All-in-One Business Platform: Unlike competitors focusing on individual applications, Zoho built an integrated ecosystem of 100+ business applications under unified data architecture.
Technical Architecture:
- Single sign-on across all applications
- Unified customer data model enabling cross-application insights
- API-first development for seamless integrations
- Common design language and user experience standards
Product Portfolio Growth:
- 2005: Zoho Office Suite (competing with Google Workspace)
- 2008: Zoho CRM (competing with Salesforce)
- 2017: Zoho One unified suite launch
- 2024: 100+ applications including ERP, analytics, and collaboration tools
Impact Metrics:
- 700,000+ paying customers across diverse industries and sizes
- 85% customer retention rate due to switching costs and integrated workflows
- $1,950 average revenue per customer (significantly higher than industry averages)
- 40% revenue growth from existing customer expansion
Pillar 2: Rural Development & Talent Strategy
Transnational Localism: Zoho pioneered developing world-class software from rural locations, creating high-value employment opportunities outside traditional tech hubs.
Implementation Approach:
- Zoho Schools of Learning: Free, practical education programs training rural youth in technology skills
- Distributed development: Major products like Zoho Desk developed entirely in rural Tamil Nadu offices
- Community investment: Supporting local infrastructure, healthcare, and education initiatives
- Leadership commitment: CEO Sridhar Vembu relocating to rural Tenkasi to demonstrate commitment
Rural Strategy Benefits:
- 15% of workforce from Zoho Schools graduates (no college degree required)
- 60-70% cost savings on operational expenses compared to metro locations
- Lower attrition rates due to stronger community connections and work-life balance
- Untapped talent access: Recruiting from pools ignored by traditional tech companies
Compare this approach with typical startup growth frameworks to understand Zoho’s unique positioning.
Pillar 3: Bootstrapped Financial Independence
Zero External Funding Strategy: Maintaining complete ownership and operational freedom by funding growth through customer revenue and profits.
Financial Discipline:
- Profitable from early years: Focus on unit economics and sustainable growth rates
- Reinvestment strategy: Allocating profits to R&D, talent development, and geographic expansion
- Pricing power: Offering 30-50% cost savings compared to competitors while maintaining healthy margins
- Long-term planning: 5-10 year investment horizons without quarterly pressure
Independence Benefits:
- Product decisions based on customer needs rather than investor preferences
- Geographic expansion to serve underserved markets rather than high-growth metros
- Talent development: Investing in education and community development for long-term sustainability
- Technology choices: Building proprietary solutions rather than acquiring for faster growth
Financial Performance:
- $1.4B annual revenue in 2024 (27% year-over-year growth)
- $400M+ estimated profit based on 30-35% margin estimates
- $12.5B valuation representing sustainable, profitable growth model
- Zero debt maintaining complete financial independence
Pillar 4: AI-First Product Enhancement
Zia AI Platform Integration: Rather than building separate AI products, Zoho integrated AI capabilities across their entire suite through Zia, their intelligent assistant.
AI Strategy Components:
- Zia Agents: Autonomous AI agents for specific business functions
- Agent Studio: Low-code platform for building custom AI agents
- Agent Marketplace: Distribution platform for third-party AI solutions
- Contextual Intelligence: AI that understands business context and user workflows
Technical Implementation:
- Privacy-first approach: Customer data processing without external LLM exposure
- RAG architecture: Retrieving relevant information while keeping data secure
- Multi-model strategy: Integrating different AI models for specific use cases
- Cost efficiency: Leveraging smaller, specialized models rather than expensive general-purpose LLMs
AI Integration Results:
- 50+ AI features deployed across Zoho suite
- 40% productivity improvement in customer support through Zia-powered automation
- 25% reduction in manual data entry across business processes
- 90% customer satisfaction with AI-assisted features
Learn more about implementing growth loops that leverage technical advantages for sustainable competitive positioning.
Pillar 5: Global Market Expansion with Local Focus
Distributed Global Strategy: Expanding internationally while maintaining strong local presence and community investment in each market.
Geographic Expansion Philosophy:
- Regional offices: Local presence in major markets (US, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, Africa)
- Cultural adaptation: Localizing products for regional business practices and regulations
- Community investment: Establishing educational and development programs in each region
- Distributed workforce: Enabling remote work from smaller cities and rural areas globally
Market Penetration Strategy:
- North America: 45.8% of revenue from largest market with Texas offices in Austin, McAllen, and New Braunfels
- Asia: 158% revenue growth making it second-largest market
- Europe: 29.7% growth maintaining strong enterprise customer base
- Emerging markets: Expanding into Africa (Lagos office) and Latin America with localized pricing
Global Results:
- 150+ countries with active customer base
- 20+ languages supported across product suite
- 12 global offices spanning 6 continents
- 24,000+ employees distributed across rural and suburban locations
Implementation Timeline: The Systematic Rollout
Phase 1: Foundation and Network Management Focus (1996-2004)
Initial Development:
- Founded as AdventNet by Sridhar Vembu and Tony Thomas in New Jersey
- Initial focus on network management software for enterprise IT departments
- Bootstrap funding through consulting and early product sales
- Building core engineering capabilities and product development processes
Early Market Validation:
- Network management tools gaining traction in enterprise market
- Revenue growth funding expansion of engineering team
- Learning enterprise software sales and support requirements
- Establishing foundational company culture and values
Key Metrics (End of 2004):
- ~50 employees primarily in Chennai, India
- $10M+ annual revenue from network management products
- Established enterprise customer base validating software development capabilities
- Strong engineering culture and bootstrap funding discipline established
Phase 2: SaaS Transformation and Suite Building (2005-2012)
Strategic Pivot to Cloud:
- Launch of Zoho Office Suite competing with Microsoft Office and Google Workspace
- Transition from on-premise software to cloud-based SaaS applications
- Building comprehensive business applications beyond productivity tools
- Establishing Zoho Schools program with first 6 rural students
Product Portfolio Expansion:
- 2005: Zoho Writer, Sheet, and Show productivity applications
- 2007: Zoho CRM and email applications
- 2008: Zoho Books accounting and invoicing software
- 2009: Company renamed from AdventNet to Zoho Corporation
- 2011: First rural office established in Tenkasi, Tamil Nadu
Growth Acceleration:
- Crossing $100M annual revenue milestone
- Expanding from productivity tools to comprehensive business management
- International expansion with US headquarters in Austin, Texas
- Building direct sales and customer success capabilities
Growth Metrics (End of 2012):
- $150M annual revenue with 30%+ year-over-year growth
- 2M+ users across productivity and business applications
- 1,500+ employees with rural development program contributing 5% of workforce
- 25+ applications covering major business functions
Compare this growth trajectory with typical startup to unicorn timelines to understand Zoho’s deliberate, sustainable approach.
Phase 3: Integrated Suite Strategy and Rural Expansion (2013-2019)
Comprehensive Suite Development:
- 2017: Launch of Zoho One integrated business operating system
- Focus shift from individual applications to unified business platform
- Significant investment in AI capabilities through Zia development
- Expansion of rural development program to multiple locations
Rural Strategy Scaling:
- 2016: Zoho Desk developed entirely in rural Tenkasi office and launched globally
- 2019: CEO Sridhar Vembu relocates to rural Tenkasi to lead by example
- Expansion of Zoho Schools to multiple rural locations across Tamil Nadu
- “Made in Rural India, Made for the World” positioning gaining global recognition
International Expansion:
- Establishing regional offices across North America, Europe, and Asia
- Localizing products for different markets and regulatory requirements
- Building regional sales and support teams
- Developing channel partner programs for global reach
Innovation and R&D:
- Major AI investments through Zia platform development
- IoT platform development for connected business applications
- Security and privacy enhancements across product suite
- Developer platform and API ecosystem expansion
Key Metrics (End of 2019):
- $500M annual revenue crossing half-billion milestone
- 50M+ users across integrated business platform
- 10,000+ employees with 15% from rural development programs
- 50+ applications in comprehensive Zoho One suite
Phase 4: AI Leadership and Global Scaling (2020-2025)
AI-First Product Strategy:
- 2025: Launch of Zia Agents and Agent Studio for autonomous business processes
- Integration of AI capabilities across entire product suite
- Privacy-focused AI approach differentiating from big tech competitors
- IoT platform launch expanding into connected device management
Market Leadership Achievement:
- 2022: Crossing $1B annual revenue milestone
- 2024: $1.4B revenue with continued 25%+ growth
- 2025: $12.5B valuation establishing unicorn status through organic growth
- Recognition as India’s second-largest bootstrapped company
Global Impact and Recognition:
- 2021: Sridhar Vembu awarded Padma Shri (India’s fourth-highest civilian honor)
- Leadership transition with Vembu moving to Chief Scientist role for R&D focus
- Expansion into Africa and Latin America with local investment programs
- Recognition as model for sustainable technology development
Current Performance (2025):
- $1.4B+ annual revenue with 25-30% growth rates
- 100M+ users across 700,000+ businesses globally
- 25,000+ employees with distributed workforce model
- 100+ applications in most comprehensive business suite globally
Learn how to track these types of metrics using proven startup KPI frameworks for sustainable growth.
Growth Metrics & Results Analysis
Valuation Growth Trajectory
Bootstrapped Valuation Evolution:
- 1996-2005: Bootstrap funding through revenue and profits
- 2010: ~$500M estimated valuation based on revenue multiples
- 2015: ~$2B estimated valuation as suite strategy gained traction
- 2020: ~$5B estimated valuation crossing billion in revenue
- 2024: $8B valuation (Hurun report previous year)
- 2025: $12.5B valuation (58% increase in one year)
Revenue Growth Performance:
- 2016: ~$240M annual revenue
- 2019: ~$500M annual revenue (doubling in 3 years)
- 2022: $1.0B annual revenue (first billion milestone)
- 2024: $1.4B annual revenue (40% growth over 2 years)
- 2026 projection: $2.0B+ annual revenue based on current trajectory
User Adoption & Engagement Metrics
User Growth Evolution:
- 2012: 2M users across productivity applications
- 2017: 25M users with suite integration strategy
- 2020: 50M users during COVID-driven digital transformation
- 2022: 80M users with AI and automation features
- 2025: 100M+ users across comprehensive business platform
Customer Metrics:
- 700,000+ paying organizations across all business sizes
- 85% annual retention rate due to integrated platform benefits
- $1,950 average revenue per customer with expansion opportunities
- 40% revenue growth coming from existing customer expansion
Market Impact & Competitive Position
SaaS Market Positioning:
- #2 player in integrated business suite category (after Microsoft)
- #3 CRM player in SMB market (behind Salesforce and HubSpot)
- #1 bootstrapped SaaS company globally by revenue and valuation
- Fastest-growing comprehensive business platform in Asia and emerging markets
Industry Transformation Impact:
- Demonstrating viability of bootstrapped growth in technology sector
- Pioneering rural development model adopted by other Indian tech companies
- Setting pricing benchmarks forcing competitors to reduce costs
- Proving customer-centric development approaches can compete with venture-backed giants
Compare these results with industry acquisition cost benchmarks to understand Zoho’s efficiency advantages.
Key Strategic Insights & Lessons
1. Bootstrapped Growth vs. Venture Capital
Strategic Decision: Maintaining complete independence through profitable growth rather than external funding.
Why It Worked:
- Operational freedom to make long-term decisions without investor pressure
- Customer-first focus prioritizing value delivery over growth metrics
- Geographic flexibility to expand into underserved markets and rural areas
- Cultural preservation maintaining company values during rapid scaling
- Sustainable pricing offering customer value while maintaining healthy unit economics
Lesson for Startups: Bootstrapped approaches can achieve significant scale when combined with disciplined growth, strong unit economics, and long-term customer value focus.
2. Comprehensive Suite vs. Point Solution Strategy
Strategic Decision: Building integrated business platform rather than competing on individual application features.
Technical and Business Advantages:
- Higher switching costs due to integrated workflows and data dependencies
- Better unit economics through cross-selling and customer expansion
- Unified development reducing engineering complexity and support costs
- Competitive differentiation through breadth rather than depth in specific features
Lesson for Startups: Suite strategies require significant initial investment but create sustainable competitive advantages through integration complexity that point solutions cannot match.
Learn more about building technical differentiation through growth loops that compound competitive advantages.
3. Rural Development as Business Strategy
Strategic Decision: Establishing development centers in rural areas while investing in local talent development and community building.
Business Impact:
- Cost advantages through lower operational expenses and real estate costs
- Talent differentiation accessing overlooked pools of capable individuals
- Employee retention through community connections and work-life balance
- Brand differentiation through social impact and sustainable development
- Government relations supporting policy objectives for rural development
Lesson for Startups: Geographic arbitrage combined with genuine community investment can create sustainable competitive advantages while generating positive social impact.
4. AI Integration vs. AI-First Product Strategy
Strategic Decision: Enhancing existing applications with AI rather than building separate AI products.
Implementation Benefits:
- Context preservation leveraging existing business data and workflows
- Privacy advantages processing customer data without external AI model exposure
- Customer adoption improving familiar tools rather than requiring new product learning
- Development efficiency enhancing proven applications rather than building from scratch
Lesson for Startups: AI integration strategies may generate more sustainable value than standalone AI products, especially for businesses with existing customer bases and proven workflows.
5. Long-Term Value Creation vs. Growth-at-All-Costs
Strategic Decision: Prioritizing sustainable growth and customer success over rapid expansion and exit strategies.
Cultural and Operational Impact:
- Employee well-being focus reducing burnout and improving retention
- Customer relationships built on long-term value rather than short-term metrics
- Product quality emphasis on reliability and customer success over feature velocity
- Market positioning as trusted partner rather than high-growth acquisition target
Lesson for Startups: Long-term orientation can achieve significant scale while building more sustainable businesses, especially in markets where customer relationships and trust are critical success factors.
Explore domain authority strategies that support long-term market positioning approaches.
Implementation Framework for Startups
When Zoho’s Bootstrapped Suite Strategy Applies
Use this approach when:
- Target market includes underserved customer segments that established players find unprofitable
- Business model supports sustainable unit economics without external funding requirements
- Product complexity benefits from integration rather than best-of-breed point solutions
- Geographic or demographic arbitrage opportunities exist for talent and operations
- Long-term customer relationships provide sustainable competitive advantages
Reference our TAM SAM SOM framework to validate bootstrapped market opportunities.
Avoid this approach when:
- Market timing requires rapid scaling ahead of well-funded competitors
- Technical or regulatory barriers require significant upfront investment
- Winner-take-all market dynamics favor rapid market share capture
- Customer acquisition costs exceed bootstrapped funding capabilities
Replicable Framework Elements
1. Sustainable Unit Economics Foundation
Customer Value Focus:
- Identify underserved customer segments with clear pain points
- Build comprehensive solutions that justify higher per-customer revenue
- Implement pricing strategies that provide customer value while maintaining healthy margins
- Focus on customer success and retention rather than rapid acquisition
Financial Discipline:
- Maintain profitability from early stages to fund organic growth
- Reinvest profits strategically in R&D, talent development, and market expansion
- Avoid unnecessary operational complexity and overhead expenses
- Build financial reserves for market downturns and investment opportunities
2. Geographic and Talent Arbitrage Strategy
Location Strategy Development:
- Identify regions with strong talent pools but lower operational costs
- Invest in local community development and education infrastructure
- Build distributed teams that leverage geographic cost advantages
- Develop remote work capabilities and culture for distributed workforce
Talent Development Programs:
- Create alternative education pathways that develop practical skills
- Invest in local talent development rather than competing for established professionals
- Build strong company culture that attracts and retains quality employees
- Develop career advancement opportunities that support long-term retention
Implement data-driven growth frameworks to optimize geographic expansion strategies.
3. Integrated Platform Development
Technical Architecture Planning:
- Design unified data models and APIs from early development stages
- Build common infrastructure and development frameworks across applications
- Implement consistent user experience and design patterns
- Plan integration touchpoints and workflow automation opportunities
Product Portfolio Expansion:
- Start with core use case and expand systematically to adjacent functions
- Build applications that leverage shared data and user workflows
- Implement cross-selling strategies based on customer usage patterns
- Develop migration paths and integration tools for existing customers
4. Long-Term Competitive Positioning
Brand and Market Strategy:
- Position as customer-centric alternative to growth-focused competitors
- Build reputation for reliability, value, and long-term partnership
- Invest in content marketing and thought leadership that demonstrates expertise
- Develop case studies and customer success stories that validate approach
Innovation and Development:
- Allocate significant resources to R&D and product innovation
- Focus on customer needs and workflow improvements over trendy features
- Build sustainable competitive advantages through technical depth and integration
- Maintain technology leadership through continuous learning and development
Action Plan: Implementing Zoho’s Bootstrapped Growth Strategy
Phase 1: Foundation and Market Validation (Months 1-12)
Customer Discovery and Validation:
- Research underserved customer segments with clear workflow pain points
- Validate willingness to pay for comprehensive solutions over point tools
- Identify geographic regions with talent and operational cost advantages
- Build initial product addressing core customer workflow inefficiencies
Financial Foundation:
- Establish sustainable unit economics with positive contribution margins
- Implement financial controls and profitability tracking from day one
- Build customer success processes that drive retention and expansion
- Create cash flow management systems for organic growth funding
Use our customer acquisition strategy guide to plan sustainable growth approaches.
Phase 2: Product Integration and Geographic Expansion (Months 13-36)
Platform Development:
- Build unified data architecture and common development frameworks
- Expand product portfolio to adjacent workflow areas for existing customers
- Implement integration capabilities and workflow automation features
- Develop APIs and developer tools for third-party integration
Talent and Location Strategy:
- Establish operations in cost-advantaged regions with strong talent availability
- Implement talent development programs that build practical skills
- Build distributed team culture and remote work capabilities
- Invest in local community development and education infrastructure
Apply three-pillar domain authority strategies for thought leadership positioning.
Phase 3: Market Leadership and Scaling (Months 37+)
Competitive Positioning:
- Establish market leadership position through customer success and innovation
- Build brand recognition as customer-centric alternative to VC-backed competitors
- Develop comprehensive case studies and thought leadership content
- Create industry partnerships and ecosystem relationships
International Expansion:
- Expand into global markets with localized product and pricing strategies
- Build regional sales and support capabilities
- Adapt products for local market requirements and regulations
- Establish local community investment and talent development programs
Success Metrics to Track
Financial and Growth Metrics:
- Monthly recurring revenue growth and customer acquisition rates
- Customer lifetime value and payback period optimization
- Gross margin maintenance during product portfolio expansion
- Cash flow generation and reinvestment allocation efficiency
Track these against startup metric benchmarks for your industry and stage.
Customer Success Metrics:
- Net revenue retention and customer expansion rates
- Customer satisfaction scores and net promoter scores
- Product adoption depth across comprehensive suite offerings
- Customer support efficiency and resolution times
Operational Excellence Metrics:
- Employee retention rates and satisfaction in distributed locations
- Product development velocity and time-to-market for new features
- Integration adoption rates and cross-product usage patterns
- Geographic expansion success and local market penetration
Conclusion: The Sustainable Growth Playbook
Zoho Corporation’s journey to a $12.5 billion valuation demonstrates that sustainable, bootstrapped growth strategies can compete successfully against venture-backed giants when built on strong foundations of customer value, operational excellence, and long-term thinking. By prioritizing comprehensive solutions over rapid feature development, rural talent development over expensive metropolitan operations, and customer success over growth metrics, Zoho created sustainable competitive advantages that traditional Silicon Valley playbooks couldn’t replicate.
The key insight for startups: Sustainable growth strategies that prioritize customer value and operational independence can achieve remarkable scale while building more resilient businesses. Zoho’s systematic approach proves that:
- Bootstrapped growth enables operational freedom and customer-centric decision making that venture capital often constrains
- Geographic arbitrage combined with genuine talent development creates sustainable cost advantages and competitive differentiation
- Comprehensive suite strategies build stronger customer relationships and higher lifetime values than point solution approaches
- Long-term value creation attracts customers seeking reliability and partnership over growth-stage vendor relationships
- Rural development models can access untapped talent while generating positive social impact and cost advantages
For startups targeting established markets dominated by well-funded competitors, Zoho’s playbook provides a proven framework for building sustainable competitive advantages through operational excellence rather than capital deployment.
The sustainable growth opportunity exists in every industry where customers value long-term partnerships, integrated solutions, and cost-effective alternatives to market leaders focused on growth over customer success.
Ready to implement sustainable growth strategies?
Explore our complete startup growth strategy guide for frameworks on choosing between bootstrapped, venture-backed, and hybrid approaches.
Learn more about building acquisition loops that create sustainable competitive advantages through customer success.
Compare your metrics with startup benchmarks by industry to set realistic growth targets for bootstrapped strategies.
Discover domain authority strategies for building thought leadership in competitive markets.
Understand India’s SaaS ecosystem and how regional strategies can drive global success.

